Shiga Toxin Producing E Coli Treatment
Shiga toxin producing e coli treatment. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli or ETEC is the name given to a group of E. Coli bacteria that produce powerful toxins which can cause severe illness. Coli STEC infect people of all ages but children under 10 years old and older adults have the most severe courses.
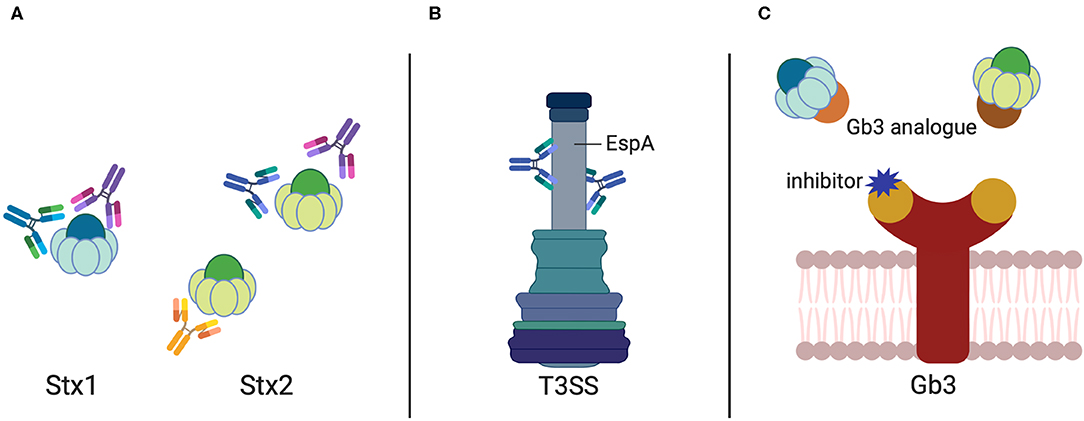
Coli STECSTEC may also be referred to as Verocytotoxin-producing E. The utility of antibiotics for STEC treatment is controversial since antibiotic resistance among STEC isolates is widespread and certain antibiotics dramatically increase the expression of Shiga toxins Stxs which are some of the most important virulence factors in STEC. The management of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli STEC infections is reviewed.
Shiga toxin-producing E. Shiga toxin-producing E. 18th June 2021 Hong Kong The Centre for Health Protection CHP of the Department of Health is today investigating a case of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli STEC infection and hence reminded the public to maintain good personal food and environmental hygiene against intestinal infections.
Coli infection The Centre for Health Protection CHP of the Department of Health is today June 18 investigating a case of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli STEC infection and hence reminded the public to maintain good personal food and environmental hygiene against intestinal infections. One of these types of E. Coli infection treatment Most infected people recover without specific treatment in five to seven days.
Treating Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli STEC gastrointestinal infections is difficult. Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli STEC is an enteric pathogen associated with human gastroenteritis outbreaks. Symptoms of STEC infection include diarrhoea stomach pain nausea vomiting and fever.
Int J Antimicrob Agents 2015. Antibiotic administration to individuals with Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli STEC infection remains controversial. Coli is known as shiga toxin-producing Ecoli or STEC.
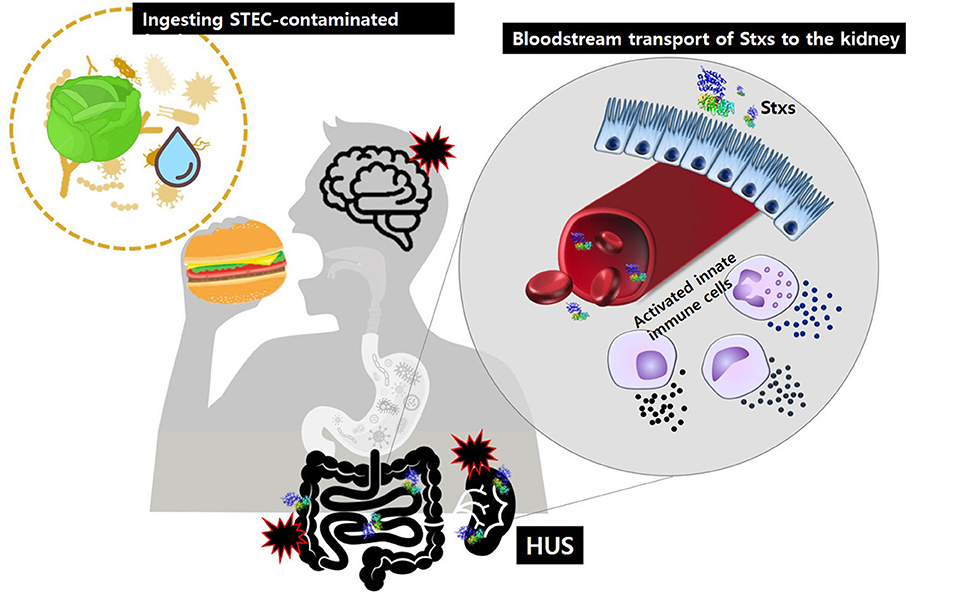
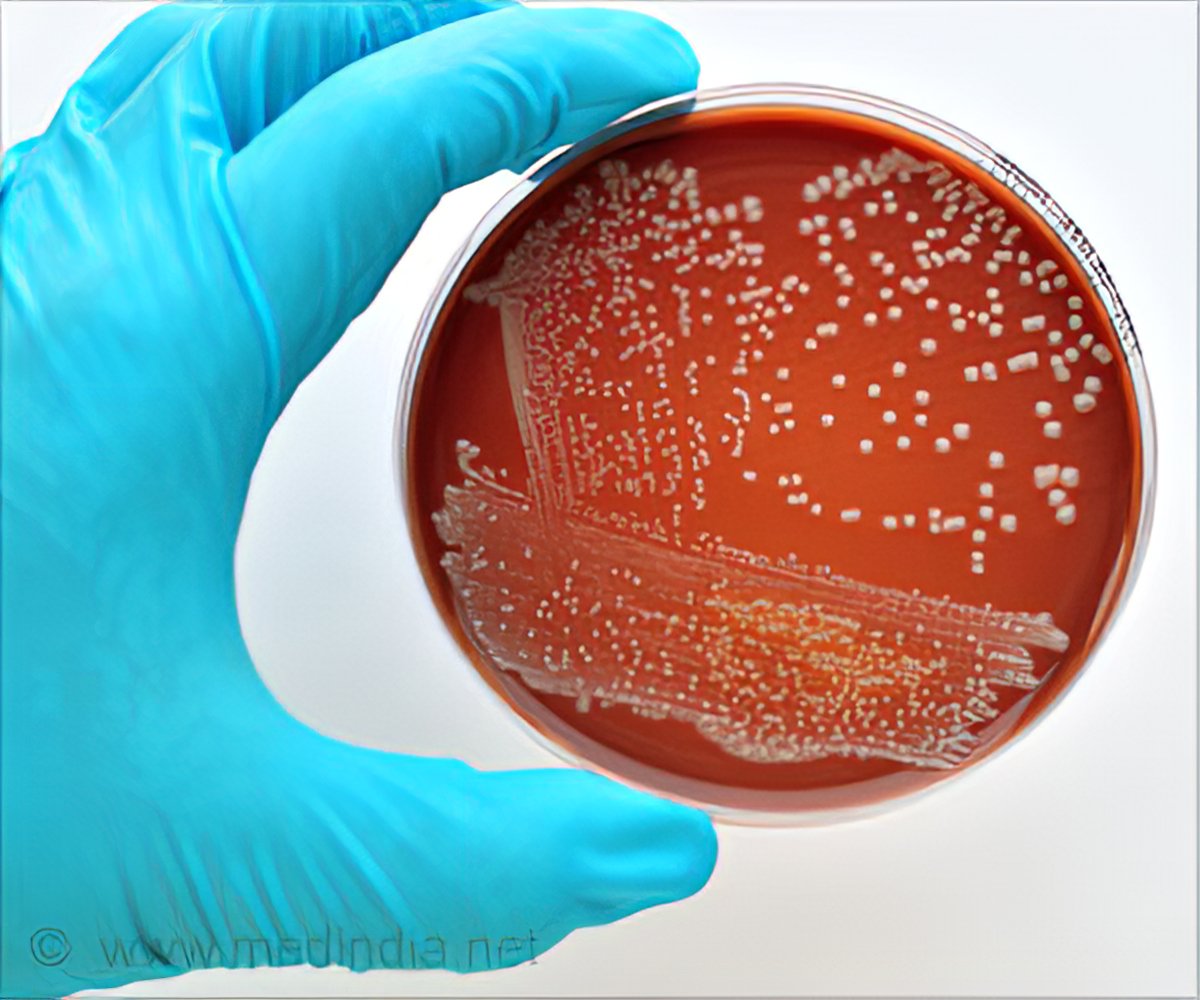
Coli O157H7 cause severe disease most notably painful bloody diarrhea and hemolytic uremic syndrome HUS. Most cases in North America are caused.
Association between azithromycin therapy and duration of bacterial shedding among patients with Shiga toxin-producing enteroaggregative Escherichia coli O104H4.
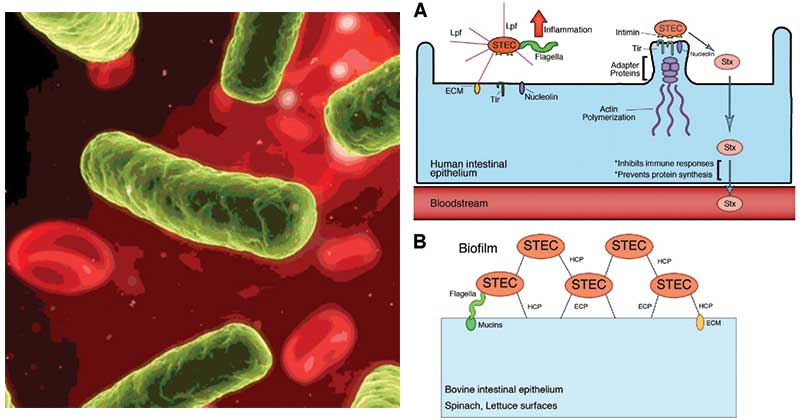
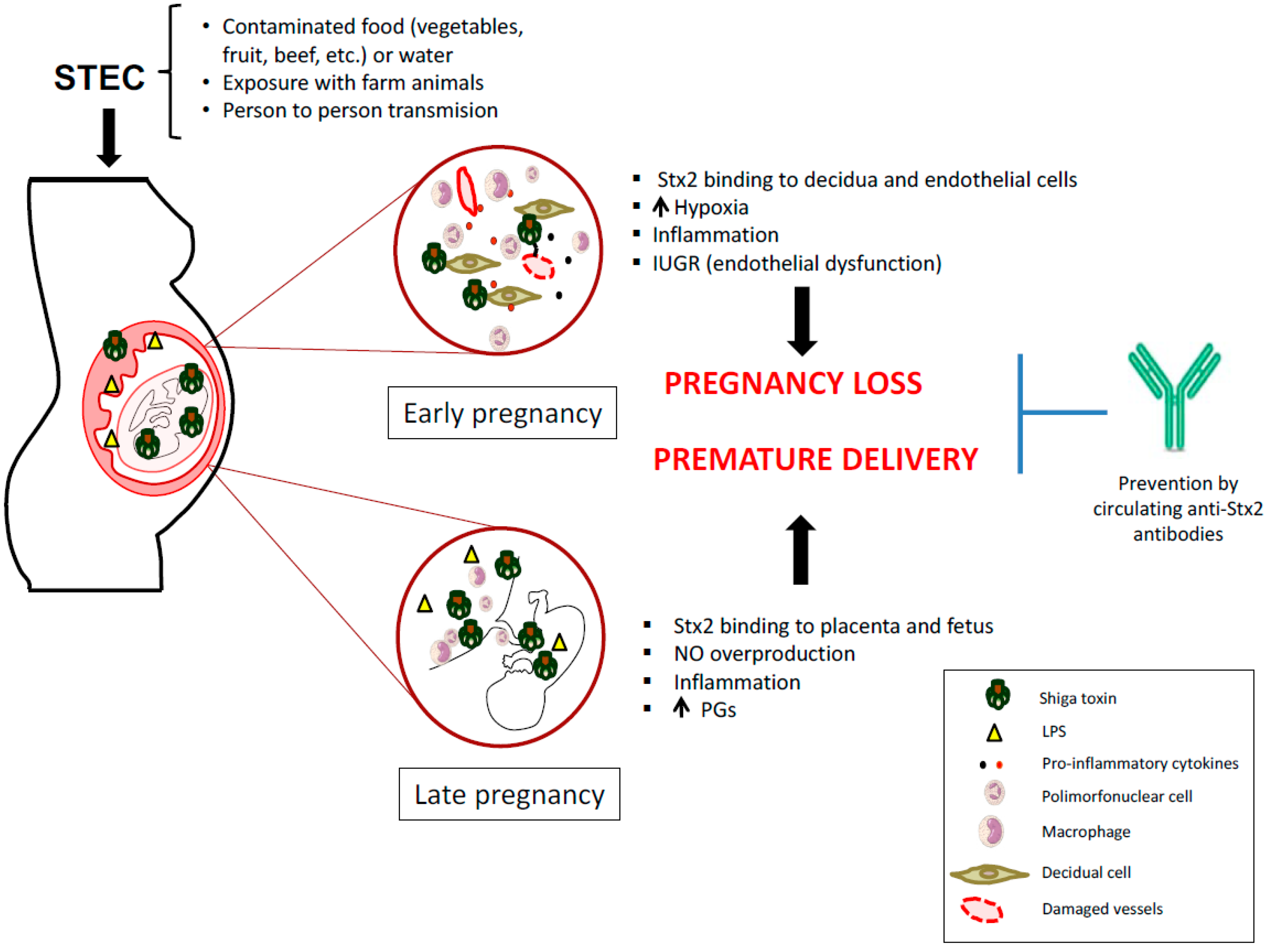
One of these types of E. Wastewater of human and animal may contain Shiga toxin-producing STEC and enteropathogenic EPEC Escherichia coli. Coli STECSTEC may also be referred to as Verocytotoxin-producing E. Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli STEC is the term used to refer to a group of E. We will summarize the literature on incidence and outcomes of these infections and then review the pathogenesis to explain the current recommendations against antibiotic use and to suggest alternative therapies. Humans can be infected with STEC by having close contact with farm animals eating undercooked beef drinking unpasteurised milk or drinking or swimming in contaminated water. CHP investigates case of Shiga toxin-producing E. Antibiotics have not been shown to improve the course of the disease and experts advise against taking antidiarrheal medications such as loperamide Imodium. Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli cause hemorrhagic colitis and hemolytic uremic syndrome.
A role for fosfomycin treatment in children for prevention of haemolytic-uraemic syndrome accompanying Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli infection. PCR screenings were performed on 12248 E. Coli infection treatment Most infected people recover without specific treatment in five to seven days. Shiga toxin-producing E. Humans can be infected with STEC by having close contact with farm animals eating undercooked beef drinking unpasteurised milk or drinking or swimming in contaminated water. The case involves a 1-year-old boy with good past health. Treating Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli STEC gastrointestinal infections is difficult.









/e-coli-symptoms-diagnosis-treatment-4174407_FINAL-5bc3f6a2c9e77c0051aa3143.png)


























Posting Komentar untuk "Shiga Toxin Producing E Coli Treatment"