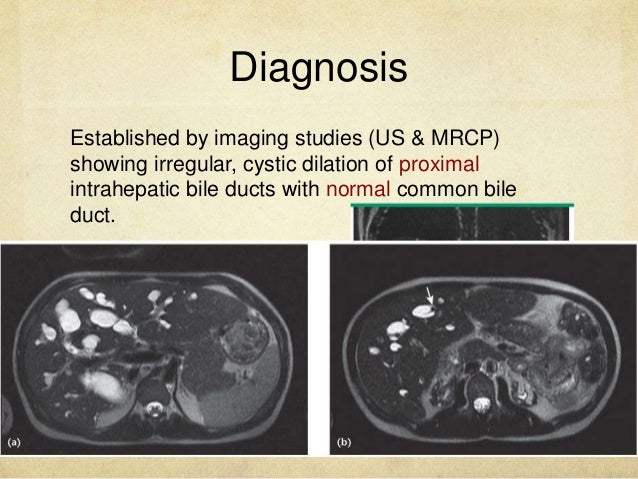
Caroli’s Disease
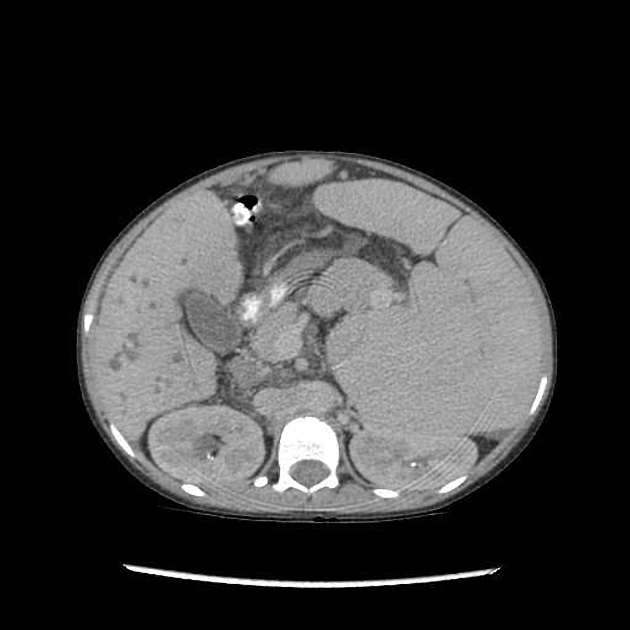
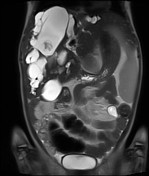
Caroli's disease. Caroli disease is a congenital disorder characterized by multifocal segmental dilatation of large intrahepatic bile ducts 12. Caroli initially described two variants which has led to some confusion in terminology. Carolis disease is defined as a congenital dilatation of the large intrahepatic bile ducts in the absence of any other features.
Carolis disease is a rare congenital hepatic disease characterized by segmental dilatation of the biliary tree. People affected by this condition experience recurrent episodes of cholestasis stone development. Descrita pela primeira vez por Jacques Caroli em 1958 é uma doença rara genética na maioria dos casos autossômica recessiva geralmente diagnosticada antes dos 10 anos de idade.
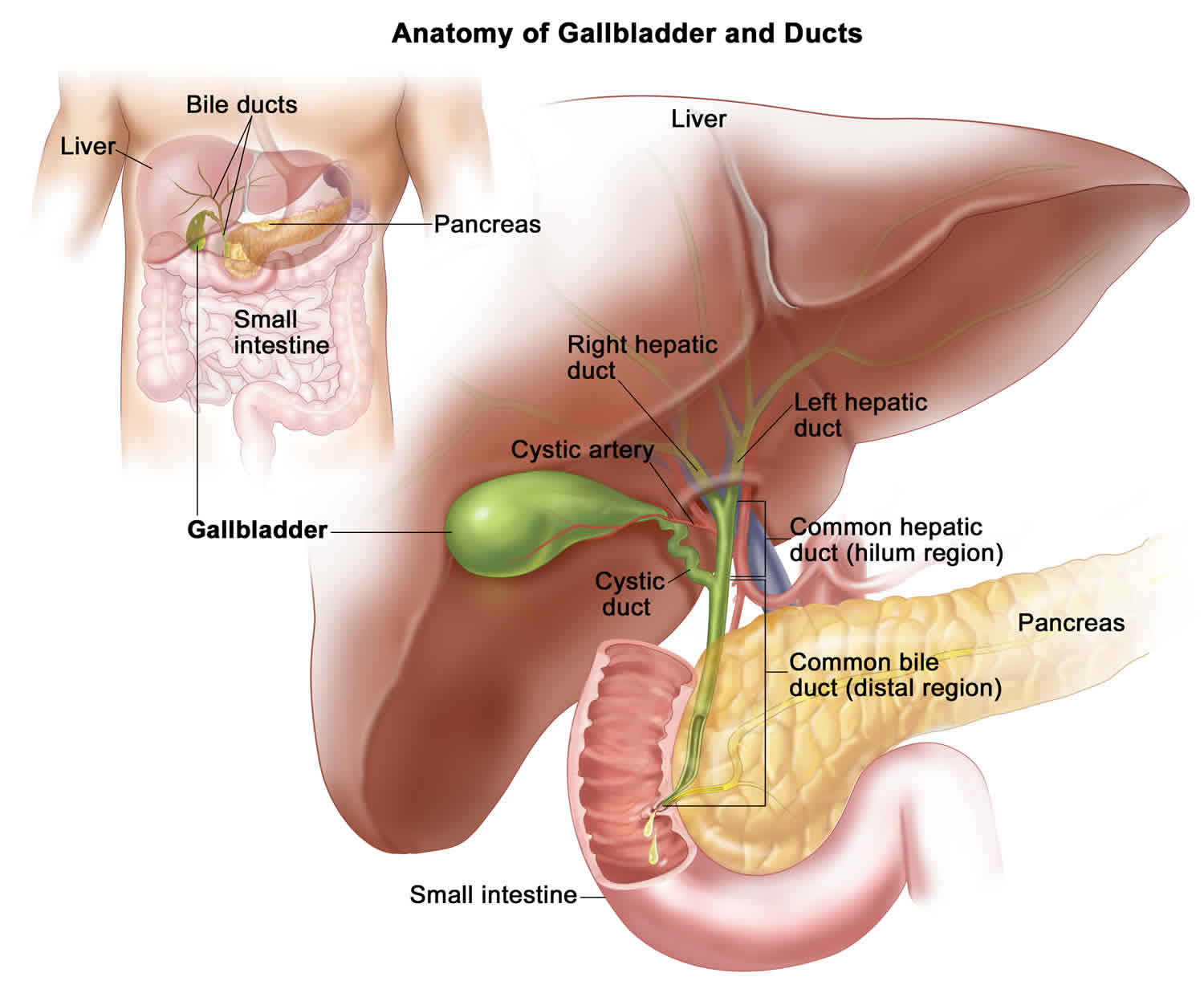
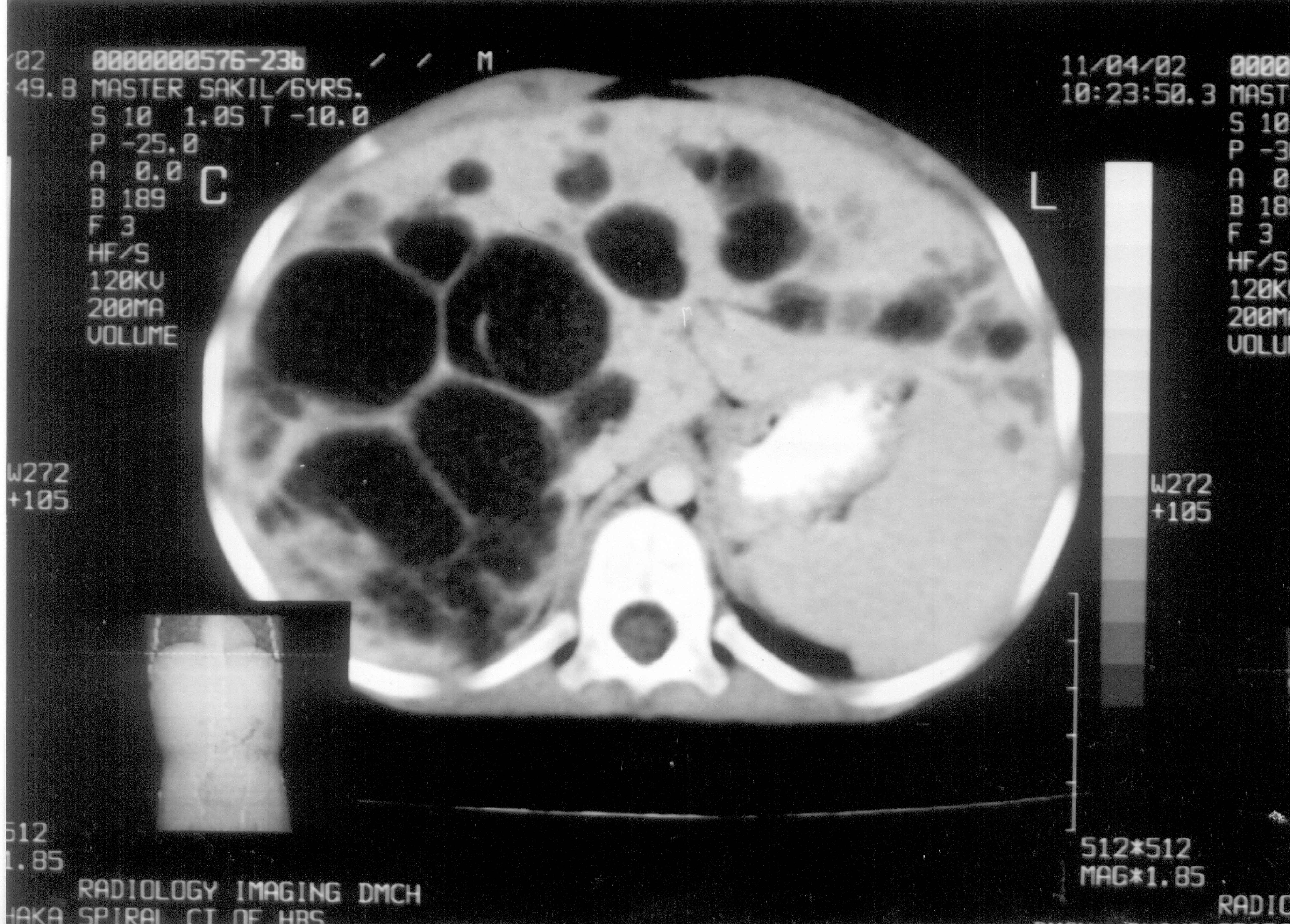
This study shows the evolution of 6 cases 2 boys and 4 giris that were diagnosed with Caroli s disease at a referral. Caroli disease is a rare inherited disorder characterize by an abnormal widening dilatation of the intrahepatic bile ducts the ducts that carry bile from the liver and renal cysts 1. The condition is usually associated with renal cystic disease of varying severity.
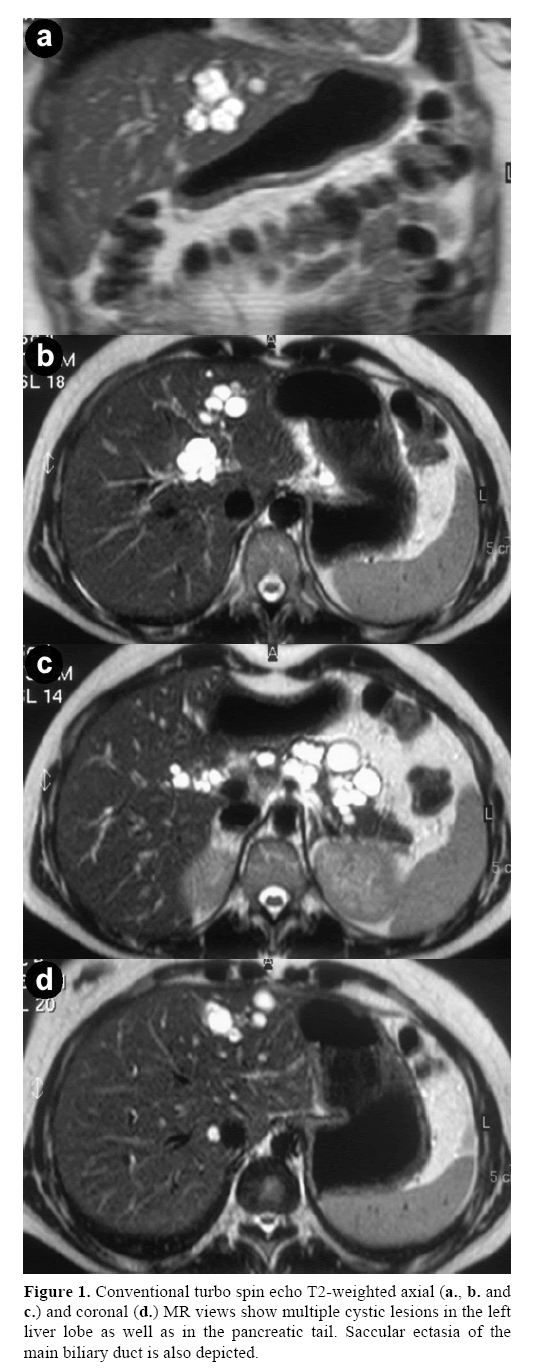
Carolis disease is a rare congenital condition chara-cterized by non-obstructive saccular or fusiform dilatation of larger intrahepatic bile ducts. 249250 These cysts represent non-obstructive saccular dilatation of the intrahepatic biliary tree 251. It is frequently associated with varying degrees of portal fibrosis corresponding to congenital hepatic fibrosis CHF.
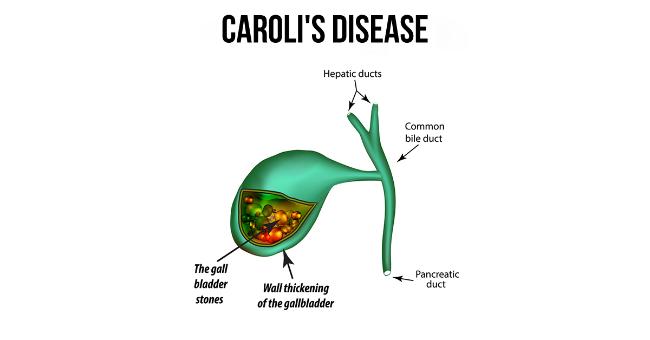
Mercadier M Chigot JP Clot JP Langlois P Lansiaux P. The most frequent clinical presentation of a simple type Carolis disease is recurrent cholangitis gallstone with pain obstructive jaundice and episodes of pancreatitis in child. Caroll s disease is characterized by congenital non-obstructive dilatation of the intrahepatic bile ducts of undefined etiology.
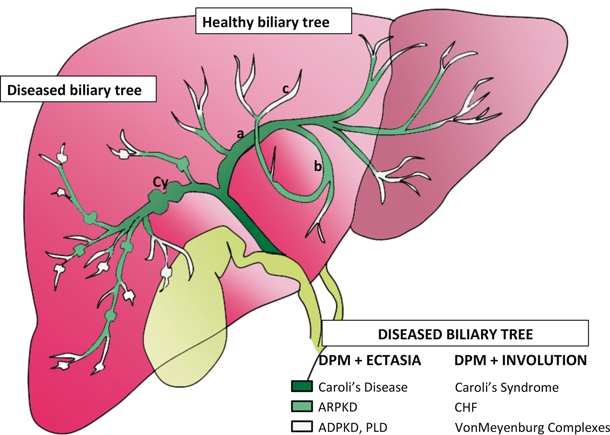
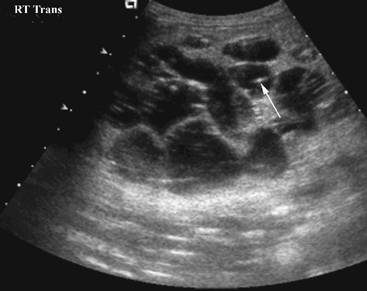
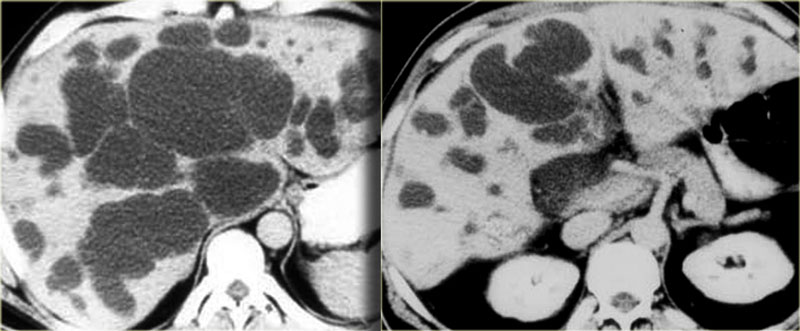
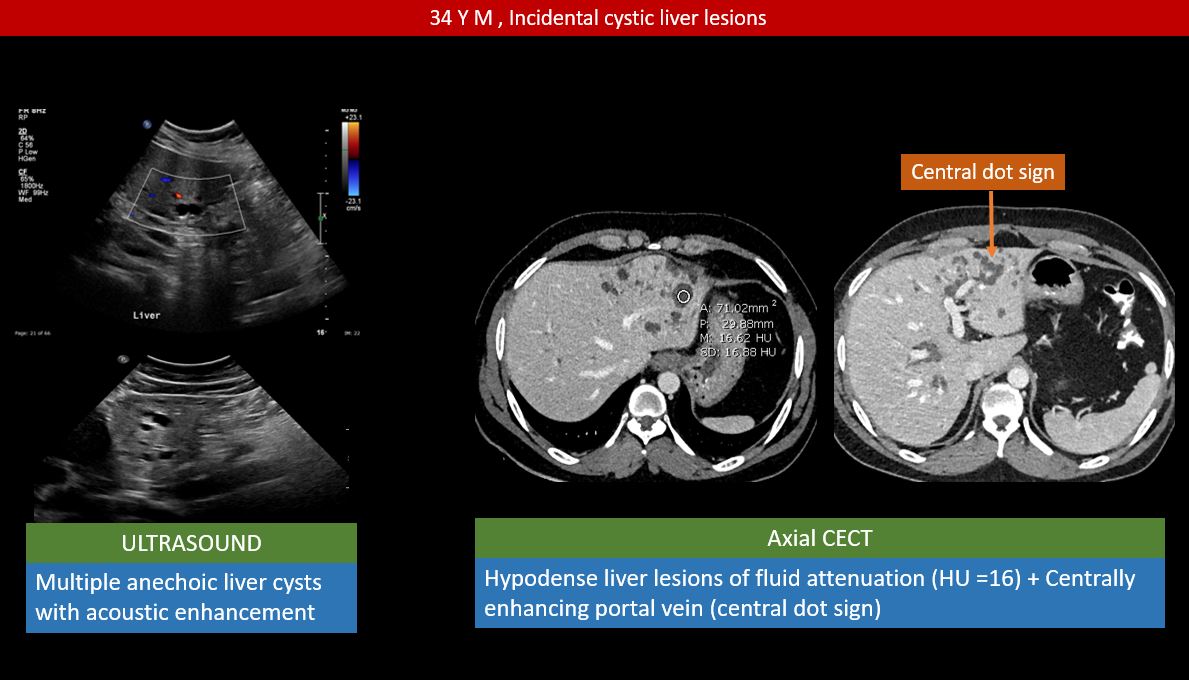
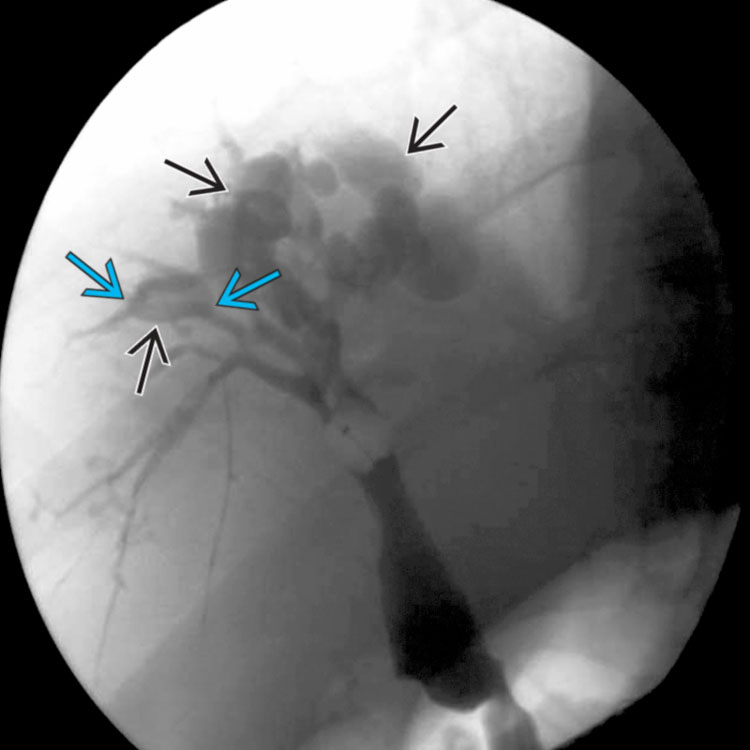
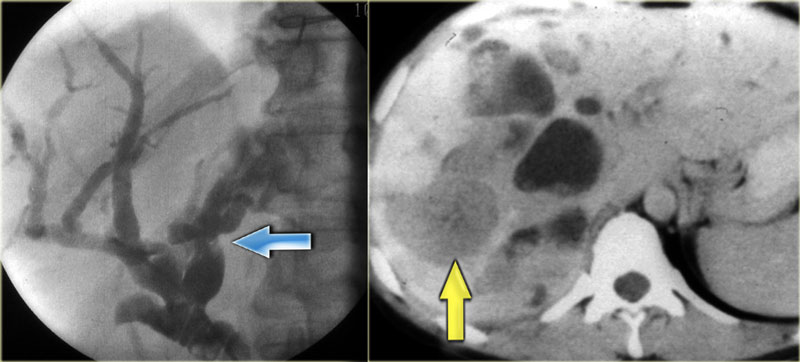
Carolis disease belongs to a group of hepatic fibropolycystic diseases 1 2. Caroli disease is a condition characterized by an abnormal widening of the intrahepatic bile ducts the ducts that carry bile from the liver and renal cysts. Although non-specific the central dot sign could be helpful to differentiate Caroli disease from other causes of focal intrahepatic biliary dilation.
Carolis disease is a rare congenital malformation characterized by multifocal dilatation of intrahepatic bile ducts predisposing to cholestasis and recurrent cholangitis. Carolis disease or communicating cavernous ectasia of the intrahepatic bile ducts is an autosomal recessive disorder and is among the ductal plate malformations that occur at different levels in the developing biliary tree leading to several clinicopathologic entities 1.
The most frequent clinical presentation of a simple type Carolis disease is recurrent cholangitis gallstone with pain obstructive jaundice and episodes of pancreatitis in child.
The most frequent clinical presentation of a simple type Carolis disease is recurrent cholangitis gallstone with pain obstructive jaundice and episodes of pancreatitis in child. The diagnosis of Carolis disease depends on demonstrating that t. Caroli disease is a congenital disorder characterized by multifocal segmental dilatation of large intrahepatic bile ducts 12. Descrita pela primeira vez por Jacques Caroli em 1958 é uma doença rara genética na maioria dos casos autossômica recessiva geralmente diagnosticada antes dos 10 anos de idade. Caroli disease is a rare inherited disorder characterize by an abnormal widening dilatation of the intrahepatic bile ducts the ducts that carry bile from the liver and renal cysts 1. Mercadier M Chigot JP Clot JP Langlois P Lansiaux P. Bile Ducts Intrahepaticabnormalities Bile Ducts Intrahepaticradiography. Caroll s disease is characterized by congenital non-obstructive dilatation of the intrahepatic bile ducts of undefined etiology. Carolis disease is a rare congenital hepatic disease characterized by segmental dilatation of the biliary tree.
Patients who have recurrent bouts of biliary infection particularly those with complications related to portal hypertension may require orthotopic liver transplantation OLT. Caroll s disease is characterized by congenital non-obstructive dilatation of the intrahepatic bile ducts of undefined etiology. Carolis disease is defined as a congenital dilatation of the large intrahepatic bile ducts in the absence of any other features. Carolis disease is a rare congenital condition chara-cterized by non-obstructive saccular or fusiform dilatation of larger intrahepatic bile ducts. Carolis disease belongs to a group of hepatic fibropolycystic diseases 1 2. The authors describe the case of a young patient with Carolis disease diagnosed by magnetic resonance cholangiography and complicated with liver abscess being submitted to. The condition is usually associated with renal cystic disease of varying severity.
































Posting Komentar untuk "Caroli’s Disease"