 Difference Between Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C | Difference Between
Difference Between Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C | Difference BetweenWhat is the difference between hepatitis B and C?Hepatitis is a virus that causes inflammation of the liver. There are different hepatitis strains, including hepatitis A, B, C and D.The most common types are A, B and C. Hepatitis A is usually a short-term infection while C can cause chronic or long-term infections. A person may have hepatitis B and at the same time. This article will examine the difference between these two viruses, available treatment options and prospects for people who have an infection. Hepatitis B and hepatitis C are both viral infections that attack the liver, and have similar symptoms. The most significant difference between hepatitis B and hepatitis C is that people can get hepatitis B from contact with the body fluids of a person who has the infection. Hepatitis C through blood contact. Neither hepatitis B nor C spreads by cough, breast milk, share food with or embrace a person who has the infection. Many people who have hepatitis do not realize until the infection has advanced. Read more about hepatitis B and hepatitis C.Hepatitis BExposure to hepatitis B virus can cause acute infection in the first 6 months. This short-term disease causes flu-like symptoms. Although it is possible to acquire hepatitis B through contact with infected blood, transmission often occurs through body fluids. The transmission of hepatitis B can occur through sex, and a woman can pass the infection to a baby during delivery. Some people can clean the virus from their system, but others will develop chronic hepatitis B.The report that the minor is when they get hepatitis B infection, most likely has a chronic infection. For example, an estimate of babies with the virus will develop a chronic infection. Other key data on CDC hepatitis B virus are: Hepatitis C can also cause acute infection. According to the (NIDDK), it is estimated that between 75% and 85% of people with acute hepatitis C will also develop chronic hepatitis C. However, around people with hepatitis C do not know they have it. Additional Key Facts about Hepatitis The C virus includes: People who received blood transfusion or organ transplantation before 1992 may also have been infected during this procedure. After 1992, doctors began to detect blood for hepatitis C before giving blood transfusions to people. Hepatitis B and C can cause similar symptoms both in acute and chronic stages of infection. The symptoms of hepatitis B in the acute phase usually occur within 6 months of the initial exposure of the virus. These symptoms may include: Some very young children with hepatitis B do not experience symptoms. About People with Hepatitis Chronic liver disease, which may include liver damage, , and .Adequate hepatitis C can cause the same symptoms as acute hepatitis B infections. However, hepatitis C is more likely than hepatitis B to become a chronic condition. Of those who have chronic hepatitis C, CDC estimates that it will develop cirrhosis, which is liver scarring. They also claim that between 1 and 5 percent of people with hepatitis C will die of cirrhosis or liver cancer. Many people may not recognize that they have hepatitis B or C until they receive detection of other blood disorders. Others may have symptoms that indicate liver problems, such as pale feces or bleeding problems. There is currently no cure for hepatitis B, but a doctor will monitor the symptoms of a person who has the infection and recommend practices that can promote liver health. Possible recommendations include: additional hepatitis B treatments depend on the specific symptoms of an individual and any complications that occur.Medics have been able to prescribe medicines that can treat hepatitis C in most people. These antiviral drugs include ledipasvir/sofosbuvir (Harvoni) and daclatasvir (Daklinza). A doctor will prescribe different medicines depending on the genotype, or variation, of the hepatitis C that a person has. It is usually necessary to take these medications for 12 to 24 weeks. There is a hepatitis B vaccine. The vaccine stimulates the body to make antibodies, or immune cells, which can fight hepatitis B infection. People at risk of exposure to hepatitis B, infants and people with infection should receive hepatitis B vaccine. Many schools and public health initiatives often offer hepatitis B vaccine to children. No vaccine available for hepatitis C. However, certain lifestyle practices can help prevent transmission of both viruses, including: Both hepatitis B and C infections can cause short- and long-term effects. However, hepatitis C is more likely to become a chronic condition than hepatitis B.A person can transmit hepatitis B through body fluids, while the transmission of hepatitis C only occurs through blood contact. A person can reduce his or her risk of hepatitis B transmission by using hepatitis B vaccine. Doctors can often treat chronic hepatitis C.If a person has risk factors for any of the forms of hepatitis, such as sharing needles, unprotected sex history, or blood transfusion before 1992, they should talk to a doctor about the tests. Last medical review on 25 October 2018Most recent newsRelated coverage
Ch. 12 Medical Overview Quiz...23cards David W.COMPANYLEGAL " POLICIESCHEG PRODUCTS AND SERVICESCHEG NETWORKCUSTOMER SERVICE© 2003-2021 Chegg Inc. All rights reserved.

Hepatitis B & C | HIV.gov
What's the Difference: Hepatitis B vs Hepatitis C? - Hepatitis B Foundation
Hepatitis B & C | HIV.gov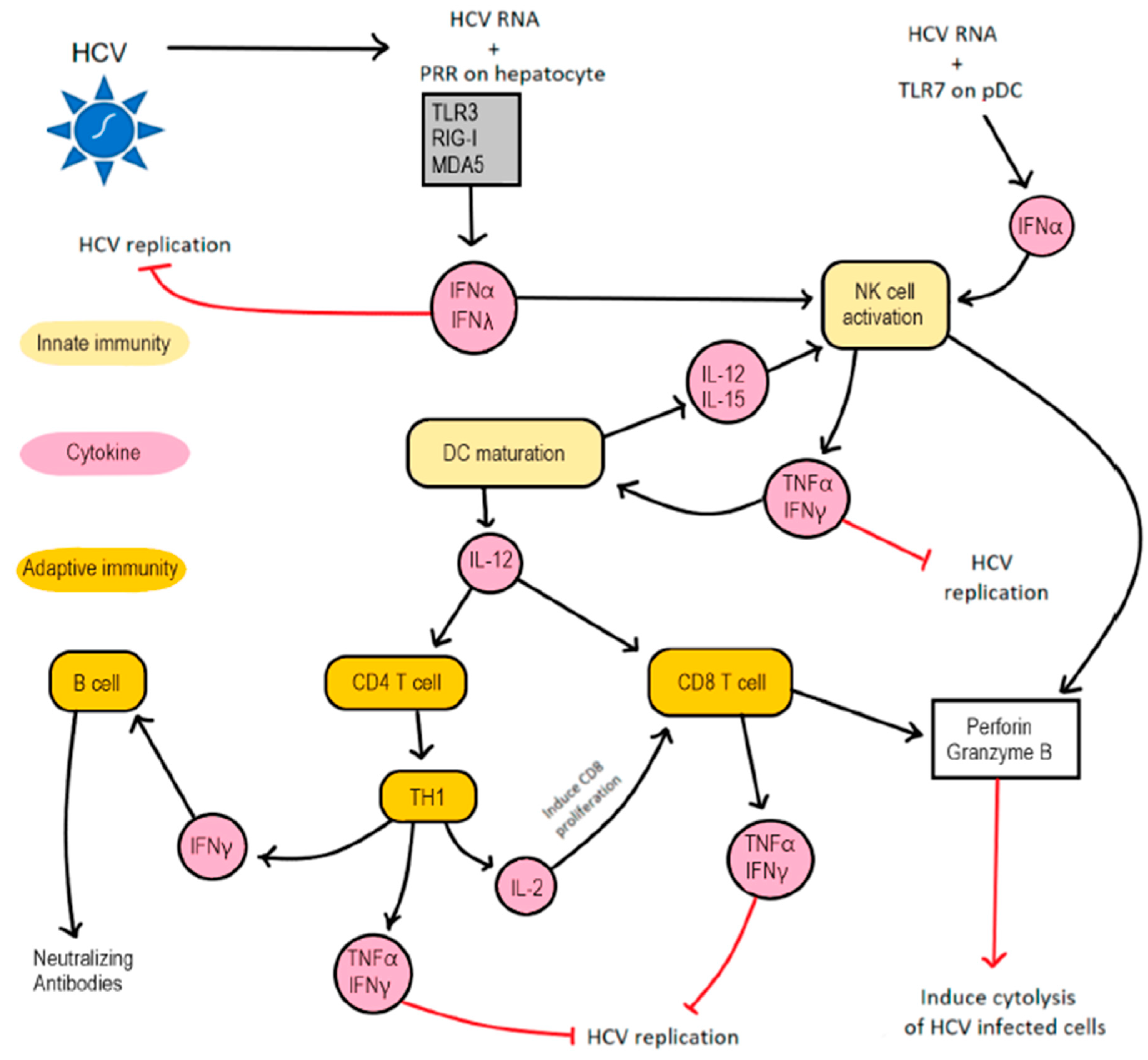
Cells | Free Full-Text | Hepatitis C Virus Infection: Host–Virus Interaction and Mechanisms of Viral Persistence | HTML
Hepatitis B vs. hepatitis C: Differences and which is worse
What's the Difference: Hepatitis B vs Hepatitis C? - Hepatitis B Foundation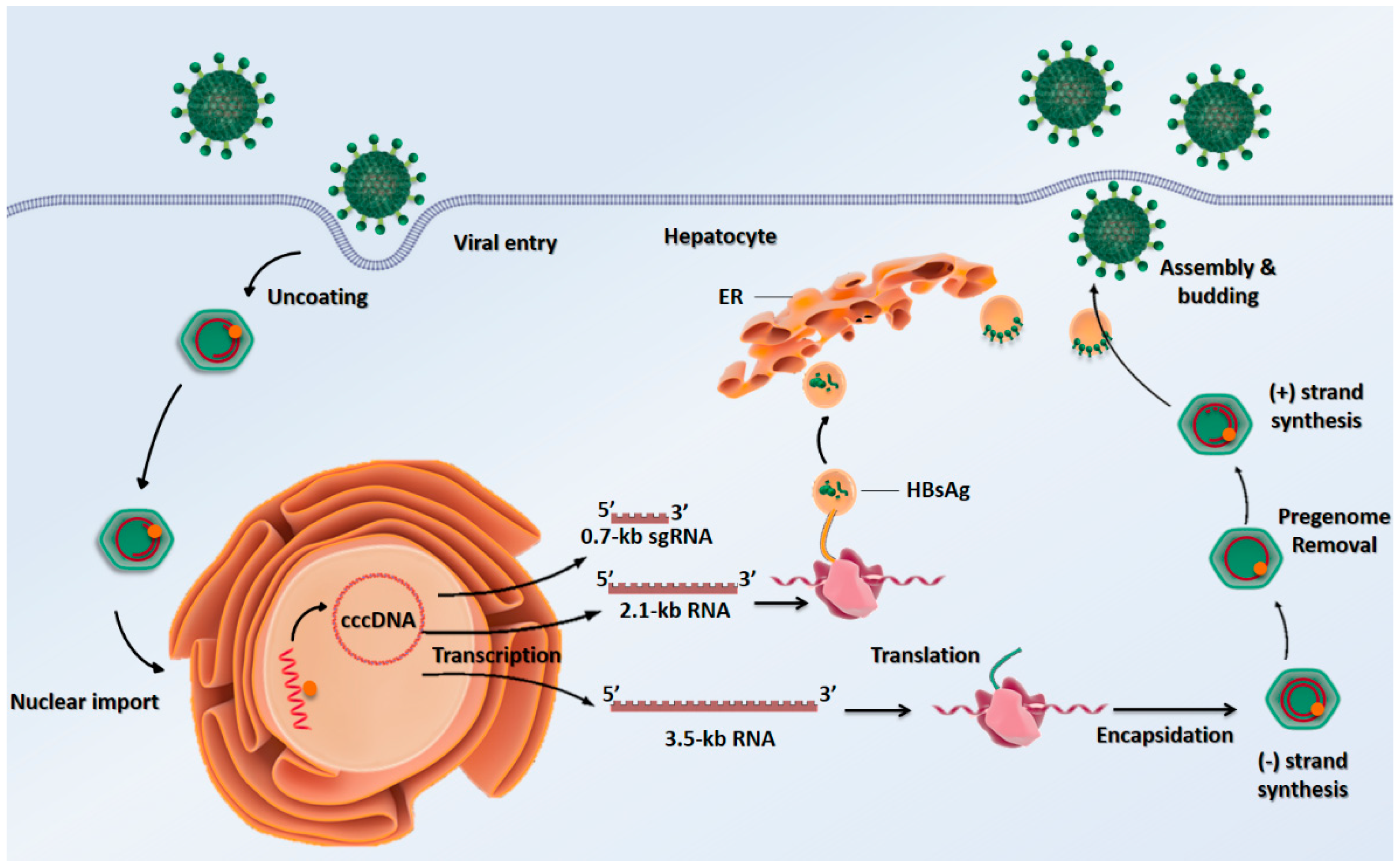
Pathogens | Free Full-Text | Hepatitis B Virus Molecular Epidemiology, Host-Virus Interaction, Coinfection, and Laboratory Diagnosis in the MENA Region: An Update | HTML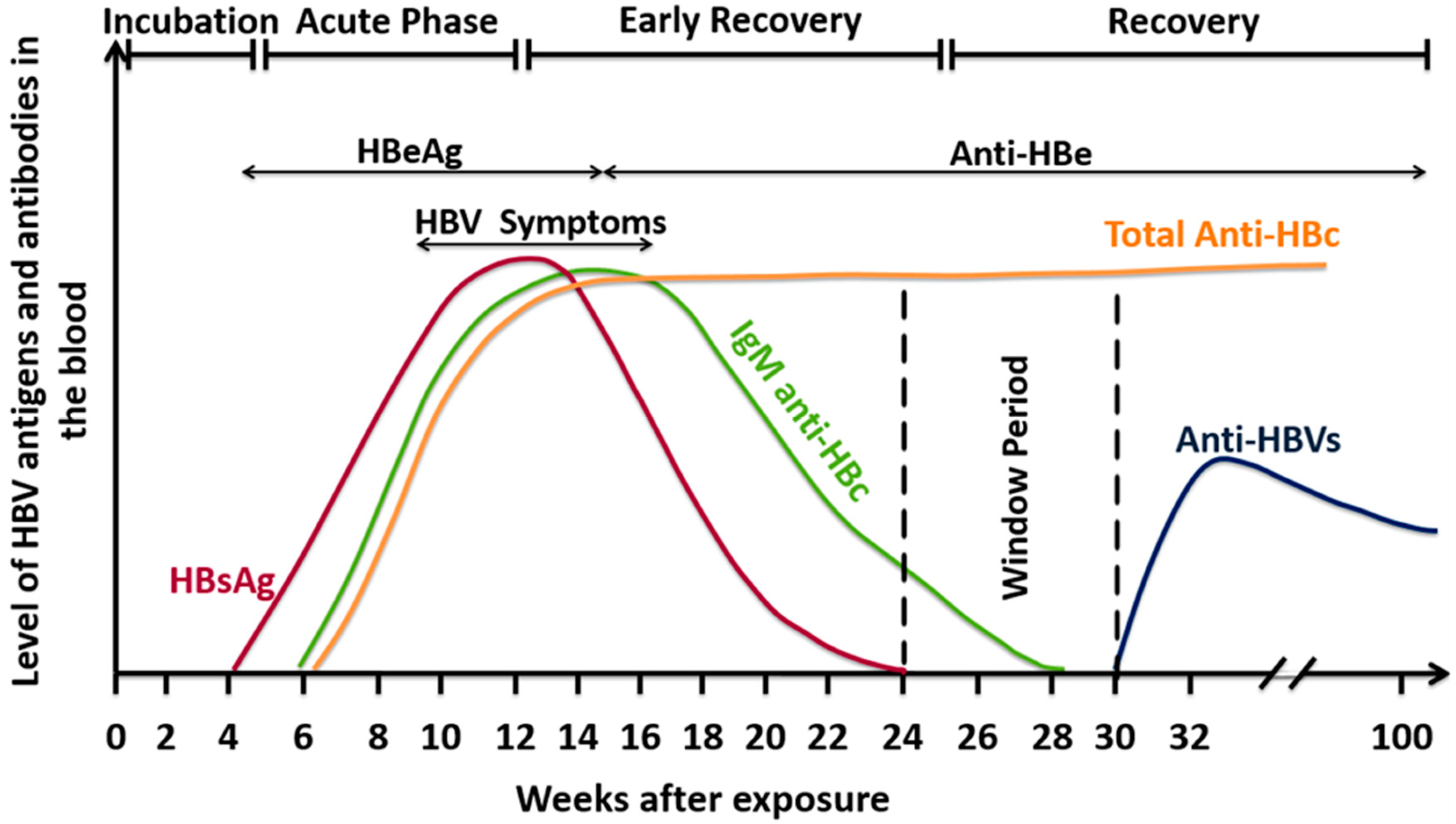
Pathogens | Free Full-Text | Hepatitis B Virus Molecular Epidemiology, Host-Virus Interaction, Coinfection, and Laboratory Diagnosis in the MENA Region: An Update | HTML
Hepatitis B Treatment: What We Know Now and What Remains to Be Researched - Suk‐Fong Lok - 2019 - Hepatology Communications - Wiley Online Library
What's the Difference: Hepatitis B vs Hepatitis C? - Hepatitis B Foundation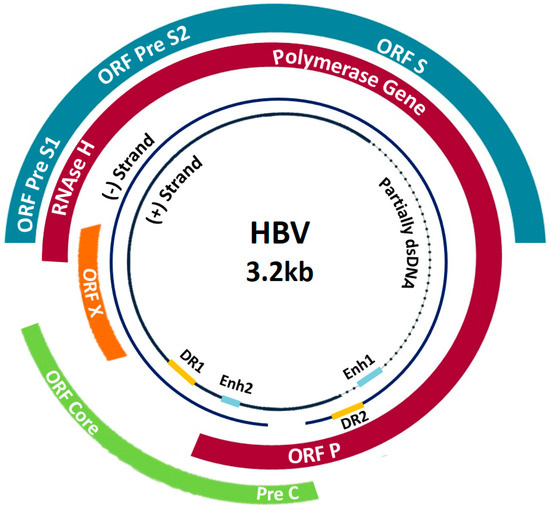
Pathogens | Free Full-Text | Hepatitis B Virus Molecular Epidemiology, Host-Virus Interaction, Coinfection, and Laboratory Diagnosis in the MENA Region: An Update | HTML
Monitoring the responses to the hepatitis B and C epidemics in the EU EEA Member States, 2019
Viral Hepatitis C: Introduction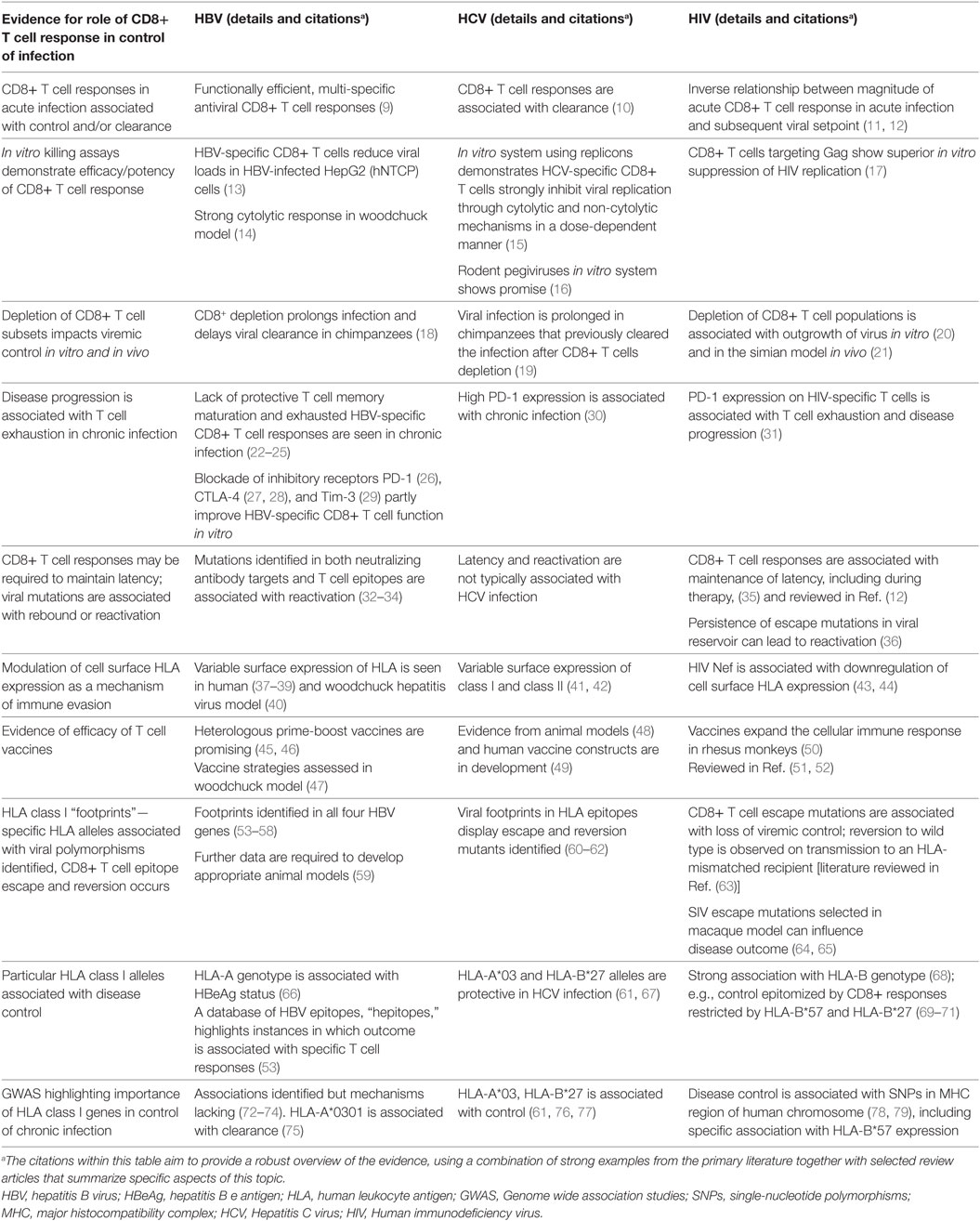
Frontiers | Hepatitis B Virus Adaptation to the CD8+ T Cell Response: Consequences for Host and Pathogen | Immunology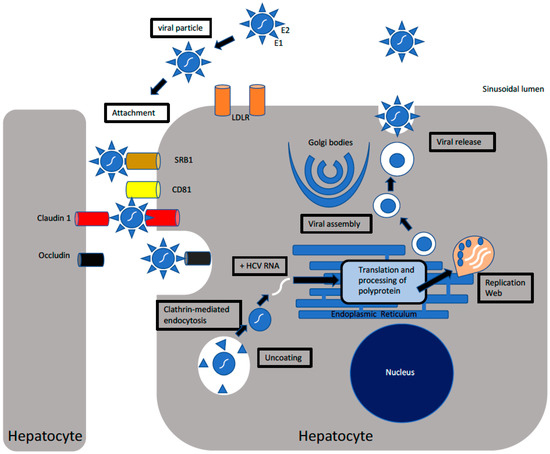
Cells | Free Full-Text | Hepatitis C Virus Infection: Host–Virus Interaction and Mechanisms of Viral Persistence | HTML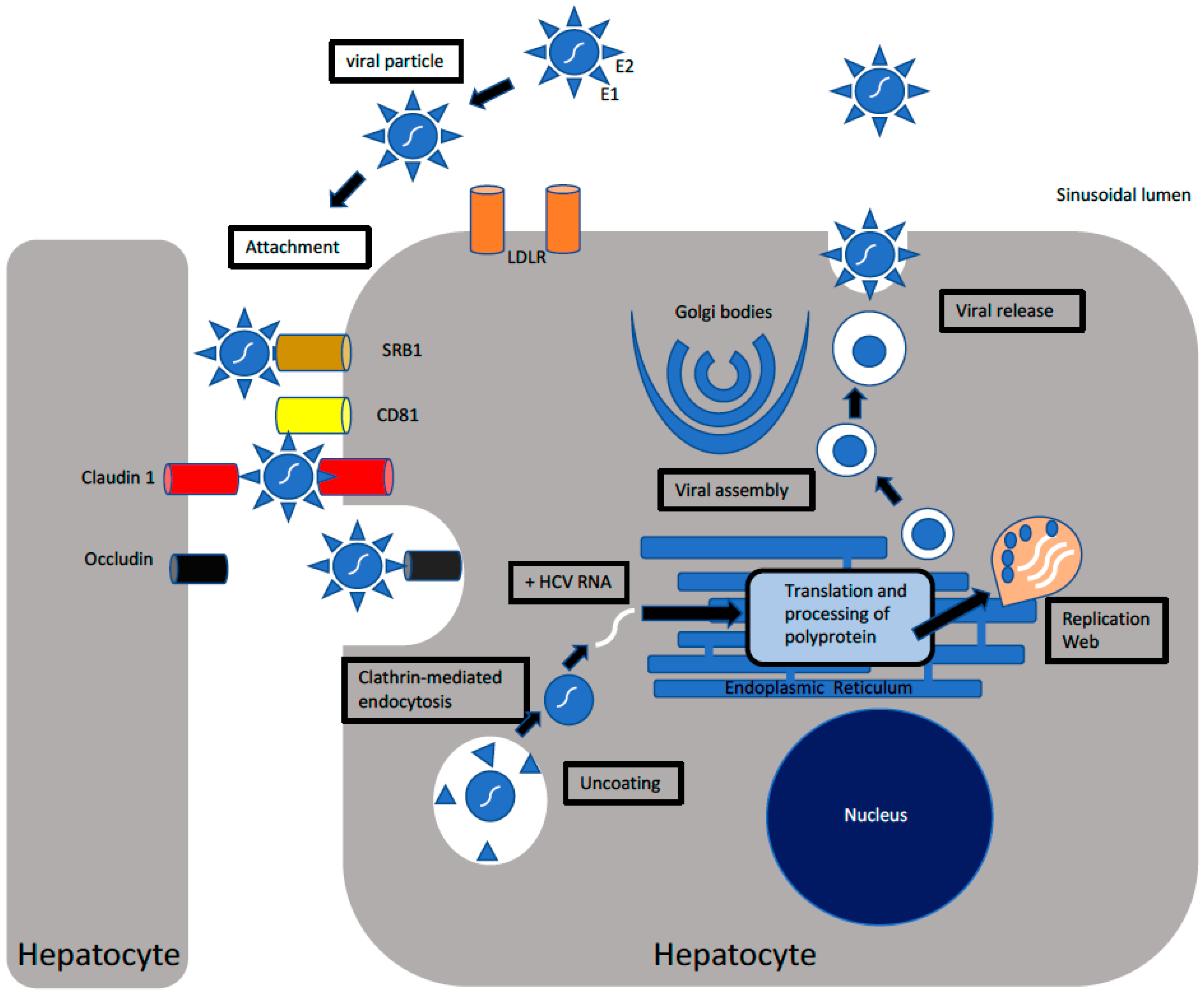
Cells | Free Full-Text | Hepatitis C Virus Infection: Host–Virus Interaction and Mechanisms of Viral Persistence | HTML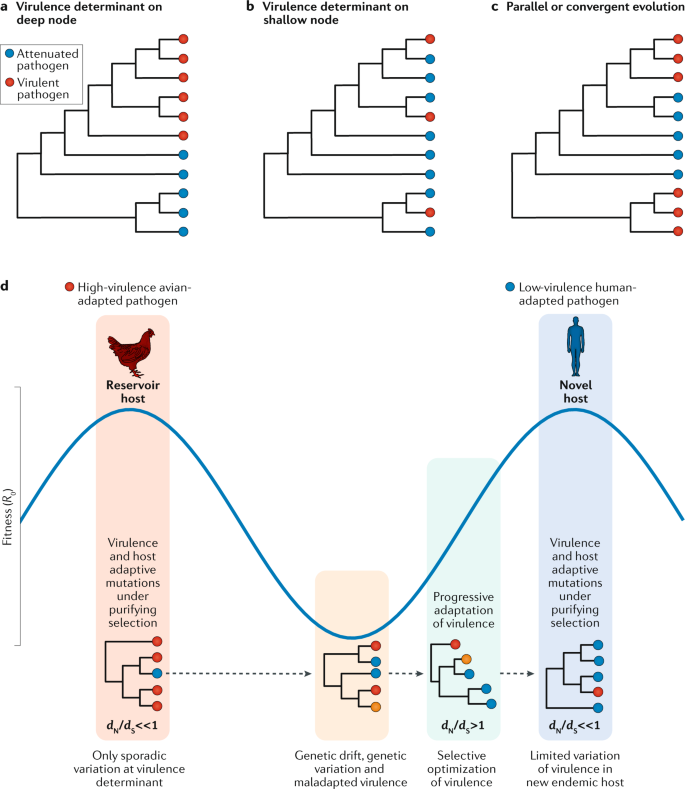
The phylogenomics of evolving virus virulence | Nature Reviews Genetics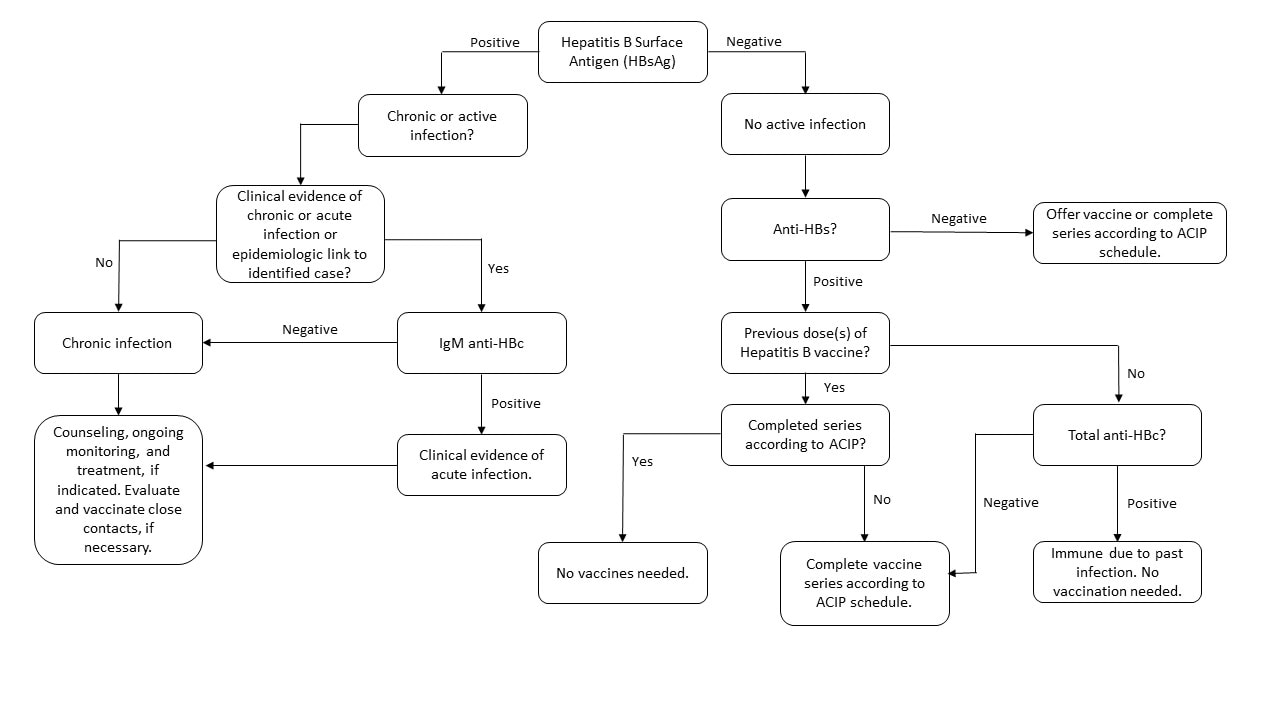
Screening for Viral Hepatitis During the Domestic Medical Examination of Newly Arrived Refugees | Immigrant and Refugee Health | CDC
The clinical virology of hepatitis B | Future Virology
The contribution of injection drug use to hepatitis C virus transmission globally, regionally, and at country level: a modelling study - The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology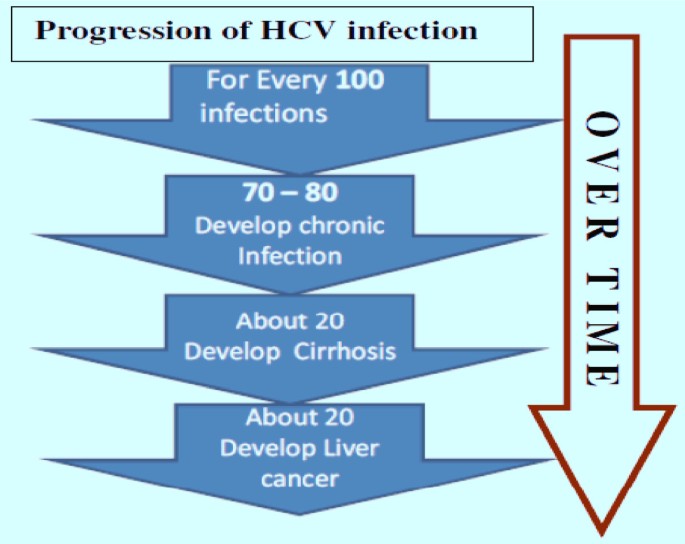
Current status and future directions in the management of chronic hepatitis C | Virology Journal | Full Text
Monitoring the responses to the hepatitis B and C epidemics in the EU EEA Member States, 2019
Naturally Occurring Mutations in Large Surface Genes Related to Occult Infection of Hepatitis B Virus Genotype C
Genotypes of hepatitis C | Hepatitis C Trust
Hepatitis B virus - Wikipedia
Approaches, Progress, and Challenges to Hepatitis C Vaccine Development - Gastroenterology
The Evolutionary Dynamics of a Rapidly Mutating Virus within and between Hosts: The Case of Hepatitis C Virus
PDF) Application of k-means clustering algorithm in grouping the DNA sequences of hepatitis B virus (HBV)
Role of hepatitis B, C, and D viruses in dual and triple infection: Influence of viral genotypes and hepatitis B precore and bas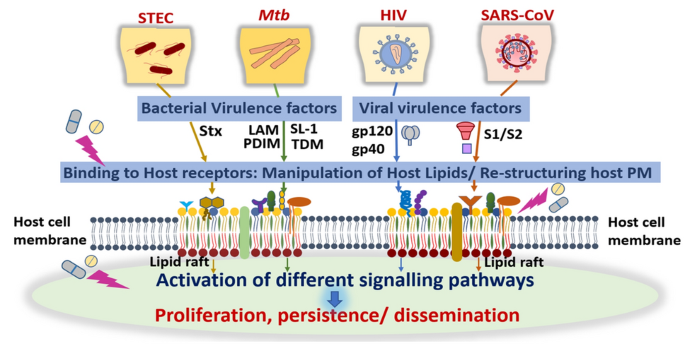
Various Facets of Pathogenic Lipids in Infectious Diseases: Exploring Virulent Lipid-Host Interactome and Their Druggability | SpringerLink
Monitoring the responses to the hepatitis B and C epidemics in the EU EEA Member States, 2019
Hepatitis B - Wikipedia
Difference Between Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C | Difference Between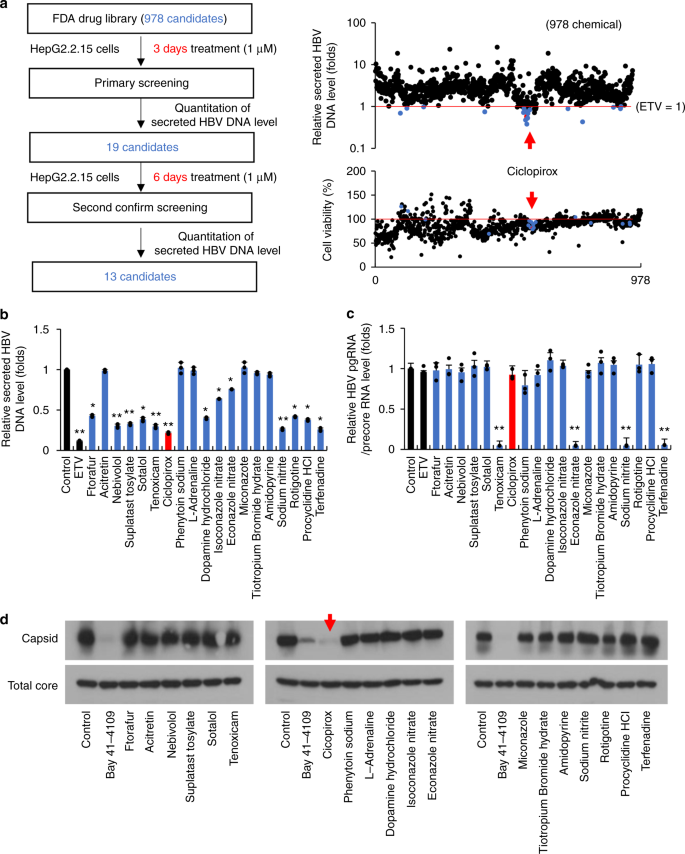
Ciclopirox inhibits Hepatitis B Virus secretion by blocking capsid assembly | Nature Communications
Induction of Prothrombinase fgl2 by the Nucleocapsid Protein of Virulent Mouse Hepatitis Virus Is Dependent on Host Hepatic Nuclear Factor-4α* - Journal of Biological Chemistry
Elucidating Novel Hepatitis C Virus–Host Interactions Using Combined Mass Spectrometry and Functional Genomics Approaches* - Molecular & Cellular Proteomics
Medical and Behavioral Approaches to Engage People Who Inject Drugs Into Care for Hepatitis C Virus Infection. - Abstract - Europe PMC
Application of k-means clustering algorithm in grouping the DNA sequences of hepatitis B virus (HBV): AIP Conference Proceedings: Vol 1862, No 1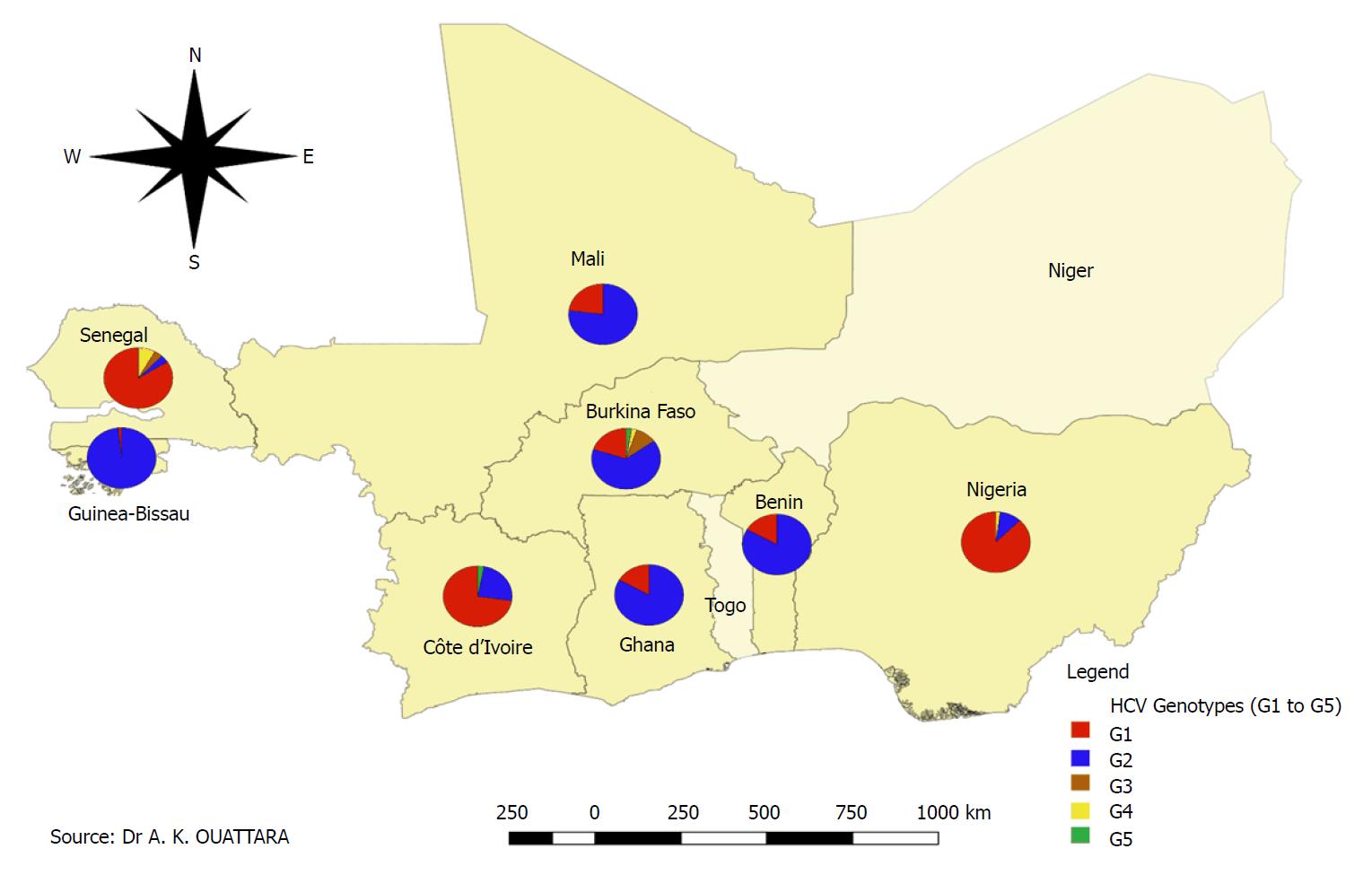
Genetic diversity of hepatitis viruses in West-African countries from 1996 to 2018
Hepatitis C - Wikipedia






























Posting Komentar untuk "hepatitis b is more virulent than hepatitis c, which means that it:"